Staying safe – information for young people, teachers and parents about vaping, alcohol, drugs and safe driving.
On this page:
- Frequently asked questions about vaping, alcohol, drugs and safe driving
- RRISK – Our program for Year 11 students about Reducing Risk, Increasing Student Knowledge
- Vaping Facts
- Reliable information for youth, teachers and parents
What are vapes?
Vapes are electronic devices designed to deliver vapourised liquids into your lungs when you breathe in.
What’s in a vape?
Vapes aren’t water. The main ingredient in vapes is propylene glycol, vegetable glycerine or glycerol, and they often also contain nicotine, flavours and other chemicals. Vapes may contain harmful chemicals that aren’t listed on the pack. The biggest misunderstanding about vapes is that they are harmless compared to cigarettes. This is not true. Vapes are not safe.
Are there vapes that don’t contain drugs? Ie. Vapes that only contains the flavour and none of the drugs.
Labels are frequently wrong. Most e-cigarettes on the market in Australia do contain nicotine, even those that claim that they don’t. E-cigarettes are unregulated, which means there are no consequences for a manufacturer who doesn’t label their product accurately. Even nicotine-free e-cigarettes are harmful to your health.
The flavours of e-cigarettes are made from multiple chemicals that are unsafe to inhale into the lungs. Inhaling chemicals can damage your airways and lungs, with the long-term damage still unknown.
Studies have shown 98% of disposable vapes confiscated in schools contain nicotine.
Doesn't vaping burn the metal coil inside and increase the chance of inhaling metal particles?
The heating coil, which allows the liquid to become an inhalable aerosol, releases new chemical substances and trace metals that go into the user’s lungs.
Studies have also shown that vapers are exposed to heavy metals such as chromium, nickel, and lead in more significant quantities than in cigarettes.
We don’t have enough evidence yet about the long-term effects of this or what happens to the other components (like the flavouring chemicals) when these are heated.
Is ‘vaping’ safer than ‘smoking’?
The most significant misunderstanding about vapes is that they are harmless. This is not true. Vapes are not safe.
Most vapes contain nicotine, making them very addictive. The amount of nicotine in one vape can be equal to the nicotine in as many as 300 cigarettes.
People who start vaping very often become dependent on nicotine. Young people who vape are 5 times as likely to take up smoking cigarettes than non-vaping young people.
Common nicotine withdrawal symptoms:
- Urges to vape or cravings.
- Restlessness of difficulty concentrating
- Sleeping difficulties and sleep disturbances
- Irritability, anger, anxiety, crying, sadness, or depression
- Increase in hunger or weight gain.
The Australian Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) has not safety-tested e-cigarettes or e-liquids, so they should not be considered safe. In some countries, people have died due to lung injury caused by using e-cigarettes.
Is vaping illegal?
Therapeutic vapes for smoking cessation and the management of nicotine dependence are only available for sale from participating pharmacies, where clinically appropriate.
It is illegal for all other retailers such as tobacconists, vape shops and convenience stores to sell any kind of vape, regardless of whether they contain nicotine.
Vapes cannot be purchased from overseas retailers or websites for personal use.
The changes are part of a wider set of vaping reforms being implemented jointly between the Australian Government and state and territory governments. They have been designed to protect young Australians and the broader community from the risks posed by vapes.
Why are vapes so addictive?
Even though they don't say it, most vapes contain high levels of nicotine, like cigarettes, which you can become addicted to very quickly and find it challenging to stop vaping.
The symptoms of nicotine addiction from vapes are the same as cigarettes and can make you feel irritable and anxious and experience intense cravings to vape. You may also experience a lack of concentration when you can't vape and have trouble sleeping.
While you might not think it, research shows you're three times as likely to start smoking if you vape.
Here is some information on nicotine dependence from smoking, which also provides information on where you can go for support. https://www.health.nsw.gov.au/tobacco/Pages/nicotine-withdrawal.aspx
For some information on drug addiction and support: https://www.health.gov.au/topics/drugs/about-drugs/what-are-the-effects-of-taking-drugs#drug-addiction-and-dependencehttps://www.health.gov.au/topics/drugs/about-drugs/what-are-the-effects-of-taking-drugs#drug-addiction-and-dependence
How do you stop vape addiction?
Most vapes contain nicotine, which makes them highly addictive like cigarettes and can make quitting difficult. If you think you may be addicted or know someone else at risk, support is available to help you get off vapes.
You can ask your GP or local youth health service for advice and support. Or you can call the Quitline on 13 7848. Our friendly Counsellors understand vaping, smoking and nicotine addiction and can provide guidance, tips, and support to help you quit.
Young Aboriginal people can call the Aboriginal Quitline on 13 78 48 to speak to an Aboriginal Counsellor and receive confidential advice and support to help them live vape-free.
How can vapes harm my health?
Vaping causes harm, including lung disease, poisoning, seizures, and burns. It can also harm your brain and cardiovascular health, including blood pressure, heart rate, and lung function. The immediate effects of vaping may include nausea, vomiting, mouth and airway irritation, chest pain, and palpitations. The cough, sore throat, dizziness, headaches, or nausea could be a sign that vaping is already doing you damage.
Vapes contain chemicals and toxins, including those that are known to cause cancer. They can also contain heavy metals and very fine particles that can harm your health. Even vapes that don’t contain nicotine (although most do) aren’t safe and can have negative, life-long impacts, especially on growing brains and bodies.
There’s evidence that adolescents may become addicted to nicotine quicker and at lower or less regular levels of consumption than adults. Adolescence is an essential time for brain development, and exposure to nicotine can have long-term health consequences, impacting memory, attention, and learning.
How do I say no to a vape?
If you don’t want to vape, you’re not alone. When someone offers you a vape, it’s good to have a reason ready to deal with pressure from friends and tell them why you don’t want to get sucked in. Here are a few:
- “Nah – nicotine gives me a headache”
- “I don’t want to get hooked like a smoker”
- “I’m trying out for the soccer team, and I don’t want vaping to ruin my chances”
Maybe make a joke or say “no thanks” plainly and firmly. Whatever works, just be prepared.
How do I find motivation to quit vaping when I know it's bad and want to stop but I also like it so I can't bring myself to quit? / How do I quit vaping?
Most vapes contain nicotine, which makes them highly addictive like cigarettes and can make quitting difficult. If you think you may be addicted or know someone else at risk, support is available to help you get off vapes.
We recommend speaking to your parent or a trusted adult. You can ask your GP or local youth health service for advice and support. Or you can call the Quitline on 13 7848. Friendly Counsellors understand nicotine addiction and can provide guidance, tips, and support to help you quit.
You can also call the Aboriginal Quitline on 13 7848 to speak to an Aboriginal Counsellor and receive confidential advice and support to help you live vape-free.
If English isn’t your first language, Quitline also has Counsellors who speak Arabic, Cantonese, Mandarin, and Vietnamese. You can also use the Telephone Interpreter Service (TIS) for other languages.
Quitting can be easier when you know what to expect. There is information you can read up that can help you quit. Many people find quitting easier when they have a plan and support from others. You can read more on this here: https://www.health.gov.au/vaping/your-questions-answered
Helpful Links:
Do you know what you're vaping? | Cancer Institute NSW
Vaping - Frequently asked questions - Tobacco and smoking (nsw.gov.au)
Generation Vape | Cancer Council NSW
E-cigarettes and young people: what you need to know (quit.org.au)
Facts about vaping (e-cigarettes) - Tackling Indigenous Smoking (tacklingsmoking.org.au)
For young people - Lung Foundation Australia
How are vapes medical and why?
Vapes have been used as a quit-smoking aid; this is when you use the vape to help you give up cigarettes. Sometimes, those who move from cigarettes to vapes become dual users, which means they end up both smoking and vaping.
How bad Is second hand vaping for you?
Second-hand vapour from vapes can contain nicotine and other harmful chemicals that have many known and unknown health risks.
Passive smoke and vapour can damage the health of anyone who breathes it in. This is especially true for babies, children and during pregnancy.
Passive smoking and vaping are never safe.
If I quit vaping but I still crave it what is a suitable substitute?
Because vapes often contain nicotine, which is an addictive chemical, certain things can trigger a desire to vape, even many years later. Social circles and certain places can be a trigger. Moving away from those triggers is a good strategy to support you to avoid vaping.
Nicotine replacement therapy (NRT) (patches, gums, lozenges, mouth spray, inhalers) may help if you are finding it challenging to manage your cravings or to quit vaping. It can be particularly helpful in the first two weeks after quitting. It is safe to use in people aged 12 and over.
Nicotine Replacement Therapy is most effective when combined with support from a health professional who can provide tips for using it. While you can buy NRT products in pharmacies and even supermarkets, you can get very cheap Nicotine patches if you get your GP (family doctor) to write you a prescription for patches. managing cravings and regularly review your progress.
Speak to your GP or pharmacist for advice.
Vaping quit support - Fact sheet for young people.
I currently store my vape in my bra stuffed somewhere discreet, where is a better spot to store it?
Whilst it’s rare, vapes can explode and cause severe burns. If you can place it in a bag or a side pocket so it is not rattling around, that is a better option as it is not on you. You want to avoid having it close to your body. This does not mean it would be safe from catching alight, but you would be lessening your own risk of injury.
If you have severe depression or anxiety, will vaping or any drug make it worse?
It is important to work closely with a health professional (GP). There are many known links between substance use and depression. Your healthcare professional will be able to assist and support you with the best way forward in relation to prescribed medication that may or may not be required. Using drugs or vaping can affect mental health, so it is best to be really honest with your GP or healthcare professional so they can provide you with the best help.
Is vaping worse than smoking?
Both have been linked with short- and longer-term health problems. Smoking causes cancer and kills. The exact effects of vaping are unknown as not enough research has been done to be clear, but short-term and longer-term health issues are being reported. Many chemicals are found in vapes, and this is where the most unknown health effects may be occurring. Find out more here:
Vaping harms your health | Cancer Institute NSW
What do you do if you’re in a house full of smokers and vapers and they don’t care about doing it around you and they won’t stop?
That can be difficult; firstly, it is helpful to know all the harms of vaping and smoking yourself so you can share those facts with your household. You can look up the facts here: Vaping – the facts https://www.health.gov.au/ If they won't consider quitting, perhaps ask if they will only smoke and vape outside or in a specific room in your home.
Will vaping make my anxiety worse?
Vaping and nicotine can impact how your brain develops, affecting your memory, attention, learning and mood. Vaping can also make mental health issues like anxiety and depression worse. There is help available if you’re experiencing mental health difficulties. You can talk to your GP or a trusted health professional or try one of these organisations:
Kids Helpline (1800 551 800)
13YARN (13 9276)
Headspace (online or phone 1800 650 890)
ReachOut (online)
Beyond Blue (online or phone 1300 224 636)
Head to Health (1800 595 212)
Are social cigarettes ok?
Social smoking is not safe. Every cigarette harms your health. If you smoke at all, you are at higher risk of heart disease and cancer than people who don't smoke.
Light and intermittent smoking, or social smoking, is less harmful than heavy smoking. However, it still increases the risks of heart disease, lung cancer, cataracts, and many other conditions.
There is also a risk of light smoking becoming more regular because people become nicotine dependent without realising it. This is the case among people who mix cannabis and tobacco.
If cannabis is always mixed with tobacco and used regularly, smokers often become nicotine dependent. They may not think of themselves as tobacco smokers, but they still have the same or higher risks as cigarette smokers (there is more tar in smoked cannabis) and the tobacco in the mull (tobacco and cannabis mix) makes them nicotine dependent.
Are you legally allowed to smoke at 16? Are you allowed to smoke cigarettes when you're under 18?
Technically, it is not illegal to smoke cigarettes if you’re under 18. It is illegal for people under 18 to buy tobacco. It is also illegal for people over 18 to buy or give anyone under 18 tobacco.
You cannot smoke in a car with a passenger under 16 years old. Heavy penalties apply.
The same applies to e-cigarettes containing nicotine.
NSW heavily regulates tobacco, cigarettes, and vaping laws. Details are provided on the NSW Health website

Do you get more drunk off spirits or beers?
Spirits contain more alcohol than beers. For example, 30ml of a high-strength spirit amounts to 1.0 standard drinks, whereas 285ml of a mid-strength beer is 0.8 standard drinks.

The drink-driving limit refers to the amount of alcohol in the bloodstream or blood alcohol concentration (BAC). This is measured in grams per 100ml. NSW has three blood alcohol concentration (BAC) limits: zero, under 0.02 and 0.05, depending on the type of license you have. Learner, P1 and P2 drivers and riders must have a zero-alcohol limit. They are more vulnerable to the effects of alcohol than experienced drivers. This means you cannot have any alcohol in your bloodstream. More information is at The Centre for Road Safety
Is methylated spirits safe to drink?
No, methylated spirits are denatured alcohol and are not safe to drink. Denatured alcohol is ethanol that has additives to make it poisonous, bad-tasting, foul-smelling, or nauseating. Drinking methylated spirits can lead to:
- headache
- dizziness
- gastric disorder (stomach problems)
- nausea
- central nervous system depression (slowed brain activity).
Large doses may cause:
- severe intoxication
- tremors
- convulsions
- drowsiness
- blurred vision
- coma
- respiratory arrest
- unconsciousness
- death.
How come alcohol makes you drunk but water doesn’t?
Water does not have ethanol, which is what makes you feel drunk.
Part of what causes people to feel ‘drunk’ on alcohol is because alcohol causes dehydration. Drinking water has the opposite effect, it hydrates your body. So if you don’t drink enough water with alcohol, you can become dehydrated quickly which would make you feel quite sick. See also the questions about hangovers. This blog explains dehydration and alcohol use in detail.
How does alcohol poison you?
Alcohol poisoning happens when you drink a large amount of alcohol, usually over a short period. Your blood alcohol concentration (BAC) is so high that it is considered toxic.
Your liver can only process about one standard drink per hour. If you drink more quickly than this, it will increase your BAC. The faster you drink, the higher your BAC will be, and the greater your chance of alcohol poisoning.
Even when you stop drinking, your BAC will continue to rise for a while. This is because alcohol in your stomach and intestines will continue to be absorbed into your bloodstream. This happens even if you are unconscious.
Drinking too much too quickly can affect breathing, heart rate, body temperature and gag reflex. In some cases, this can lead to a coma and death.
What about ‘tactical vomits’ or ‘tacs’- do they sober you up faster?
While you may feel a little better straight after a ‘tactical vomit’, the effect won’t last long. It does not sober you up.
Vomiting can be life-threatening, and when you force yourself to throw up, it can be damaging to your body. This includes inflammation, tears, and bleeding to your oesophagus (food pipe) or eye damage.
Paul Dillon’s blog on tactical vomits answers this question in more detail.
Why do you feel better after vomiting?
Vomiting after drinking may reduce the stomach pain that the alcohol has caused. If you throw up shortly after having a drink, your body may not have absorbed the alcohol, potentially lessening its effects.
Vomiting is your body’s response to excess toxins from alcohol in your body. However, the effects are short-term, and the risks of throwing up after drinking alcohol greatly outweigh any possible benefits.
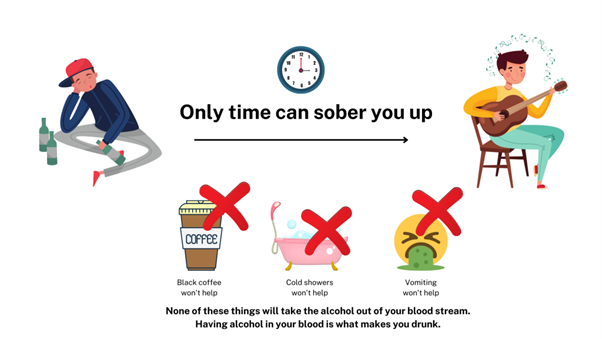
Does vaping help sober you up?
No. In fact, vaping can be harmful.
Sobering up, or getting the alcohol out of your body, takes time. About 10% of alcohol leaves the body in breath, sweat and urine, but the liver breaks down most.
The liver can only eliminate about one standard drink per hour. Nothing can speed this up—not even black coffee, cold showers, exercise, or vomiting.
You can still be over the legal limit even a few hours after your last drink, even if you feel okay. The NSW Centre for Road Safety talks more about how long it takes you to sober up.
Is there anything that can help you pass an RBT? I’ve seen kits that you can buy on the web that say they can help you get a negative test.
Nothing will bring your BAC down enough to pass a test if you are over the limit.
There are lots of things that claim to be “hacks” to reduce your Blood Alcohol Concentration (BAC). None of these will work, especially if your limit is zero!
The NSW Centre for Road Safety goes into more detail about why you can’t make your body process alcohol faster: “There is no way to speed up the rate your body gets rid of alcohol. While small amounts of alcohol leave your body in your urine, sweat and breath, your liver breaks down most of the alcohol. A healthy liver breaks down less than one standard drink per hour. If your liver is damaged, it takes even longer.
Black coffee, showers, water, or food will not work. The only thing that sobers you up is time. After a big night out, you may still be over your legal alcohol limit for much of the next day.
After a heavy night of drinking, it can take more than 18 hours for your blood alcohol concentration to get back to zero. Many people are booked for drunk driving the next day."
What causes a hangover and is there any way you can prevent or reduce one?
The only way to completely avoid a hangover is not to drink alcohol at all. Drinking in moderation, i.e. less than one or two standard drinks, is the next best way to avoid a hangover. Only time will cure a hangover.
This factsheet covers several factors that can contribute to hangovers:
- Mild dehydration can cause thirst, fatigue, and a headache.
- You become dehydrated because alcohol makes you urinate more, so you lose more body fluids. Drinking water between alcoholic drinks is a good strategy to prevent these symptoms.
- Disrupted sleep leads to fatigue.
- You may fall asleep faster after drinking alcohol, but sleep is fragmented, and you tend to wake up earlier, so you won’t feel rested at all.
- Gut irritation can cause nausea and tummy pain.
- Alcohol directly irritates the lining of the stomach.
- Inflammation can lead to malaise (generally feeling unwell).
- Alcohol increases inflammation in the body. Inflammation contributes to the malaise that people feel when they are sick, so it may also play a role in hangover symptoms.
- Acetaldehyde exposure can lead to inflammation in organs.
- When the liver breaks down alcohol, it creates the compound acetaldehyde. This is a toxic, short-lived by-product that leads to inflammation in the liver, pancreas, brain, gastrointestinal tract, and other organs.
- Mini withdrawal can make you feel restless and anxious.
- While drinking, you may feel calmer, more relaxed, and even euphoric, but the brain quickly adjusts to those positive effects to maintain balance. So when the buzz wears off, people can feel more restless and anxious than before they drank.
Because we all break down alcohol differently, it is hard to know how many drinks will cause a hangover. Any time you drink until you are “drunk”, there is a chance you could have a hangover the next day.
There is no way to speed up the brain’s recovery from alcohol use—drinking coffee, taking a shower, or having an alcoholic beverage the following day will not cure a hangover.
To help ease hangover symptoms, some people drink electrolyte-rich sports drinks to try to treat electrolyte imbalance caused by fluid loss from drinking. However, the impact of these drinks on hangovers is debatable. In most people, the body will quickly restore electrolyte balance once the effects of alcohol subside.
I’ve seen things at the chemist that say they are ‘hangover cures’ - do they work?
Although popular remedies like those you see at a chemist might make your hangover symptoms lessen, no medication can ‘cure’ a hangover.
Check out this expert review of five hangover ‘cures’.
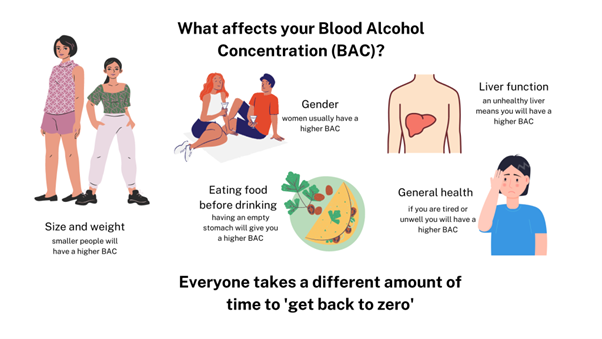
How does height and weight affect alcohol absorption?
How quickly you absorb alcohol depends on different factors, like:
- your age and sex
- your body size, weight, and composition
- your experience with alcohol
- if you have taken medicines or other drugs and your liver health.
Alcohol also affects people differently. Two people who drink the same amount can have different BACs. This is due to factors such as:
- Size and weight – a smaller person will have a higher Blood Alcohol Concentration from the same amount of alcohol.
- Gender – a woman the same height and weight as a man, drinking the same amount, will have a higher BAC.
- Liver function – an unhealthy liver will process alcohol slower than a healthy liver.
- Recent consumption of food – lack of food in your stomach means you'll absorb alcohol into your blood faster.
- Fitness, fatigue, and general health condition – your BAC can be higher if you feel unwell, tired, stressed or unfit.
For more information, see How alcohol affects your health | healthdirect
Why does it take longer for females to process alcohol?
There are several reasons for this. Women's bodies contain proportionately less water and more fat than men's bodies. Water dilutes alcohol, and fat retains it, so women's organs are exposed to higher concentrations of alcohol for more extended periods. Also, women have less alcohol dehydrogenase, an enzyme that breaks down alcohol before it reaches the bloodstream. At any given dose, women's blood levels of alcohol will be higher than a man's, even considering differences in body weight. As a result, one drink for a woman is roughly equivalent to two drinks for a man.
Everyone's body is different and will process drugs and alcohol differently, so drugs won't necessarily have the same effect on people. That's why taking drugs is risky and can cause adverse reactions.
Generally, females have smaller body sizes so get drunk more quickly than males.
https://www.drinkaware.co.uk/facts/health-effects-of-alcohol/general-health-effects/alcohol-and-women
Scientists have discovered that women produce smaller quantities of an enzyme called alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH). This enzyme is released in the liver and breaks down alcohol in the body.
How long is it for a female if they had 12 drinks to return to zero?
How quickly your body processes alcohol depends on lots of different factors. Not every person will take the same time to ‘get back to zero’.
Two people who drink the same amount can have different Blood Alcohol Concentrations (BACs). This is caused by factors such as:
- Size and weight – Generally, a smaller person will have a higher BAC from the same amount of alcohol.
- Gender – generally, a woman the same height and weight as a man, drinking the same amount, will have a higher BAC.
- Liver function – an unhealthy liver will process alcohol slower than a healthy liver.
- Recent consumption of food – lack of food in your stomach means you will absorb alcohol into your blood faster. However, eating food after you have been drinking will not reduce your BAC.
- Fitness, fatigue and general health condition – your BAC can be higher if you are not feeling well, you are tired, stressed or unfit.
This example is from Transport for NSW.
“Melita is 18 and holds a P1 license with a zero-alcohol limit. She started drinking at 10pm and had 6 mixer (9 standard) drinks over 4 hours.
At 2am her blood alcohol concentration was 0.24. She stayed the night at a friend’s house.
It took more than 16 hours before Melita’s BAC was back to zero. Melita had to get her mum to drive her to work that morning. She had to wait until 6pm that night before she could drive.”
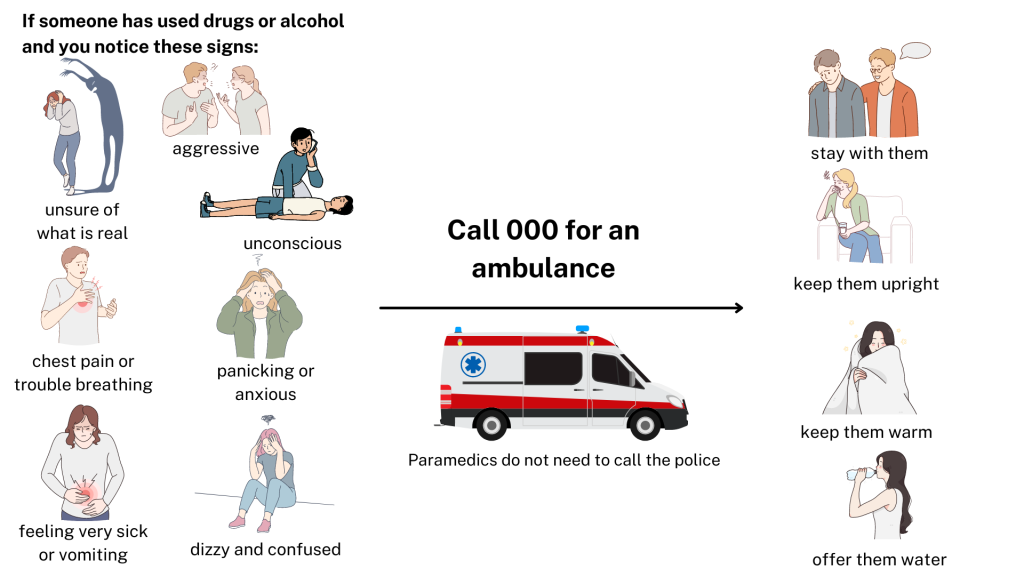
What do we do if the drunk person is being resistive and doesn’t want help? What do you do with a temperamental drunk?
Not all drunk people want to be looked after, and some can be extremely difficult to deal with. Some people become aggressive when they drink and are potentially dangerous.
Your first priority must always be your personal safety. Never put yourself in a situation where you could get hurt.
If your friend does not want your help, involve someone else and try to work as a team. If you are really worried about their safety, call 000.
For more advice, check out this factsheet from DARTA.
What if you are in a scenario where there is no chair to do the drunkenness test on?
The chair drunkenness test is a simple test where the drunk person is seated in a normal armless chair. If they can’t hold their body and head up without support, they need to be placed into the recovery position. If they can, they still need to be monitored while they sit for any sign of slumping.
This factsheet from DARTA recommends that if you think your friend is drunk, keep them as upright as possible. Never lay them down on their back as they are difficult to monitor. If they vomit even a small amount, there is a very real risk of choking.
If your friend is so drunk that they are unable to sit up, place them on their side in the recovery position and watch them carefully.
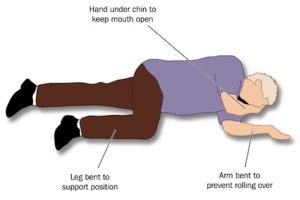
The recovery position helps to ensure a clear airway for breathing and to prevent inhalation of vomit. Image credit: healthnavigator.org.nz
If someone shouldn’t be put to bed when they are drunk, what do you do if they are struggling to stay awake? Call an ambulance?
The chair drunkenness test is a simple test where the drunk person is seated in a normal armless chair. If they can’t hold their body and head up without support, they need to be placed into the recovery position. If they can, they still need to be monitored while they sit for any sign of slumping. If your friend is so drunk that they are unable to sit up, place them on their side in the recovery position and watch them carefully.
If they are unconscious or not breathing, call an ambulance. If in doubt, call an ambulance. For more info, see https://darta.net.au//wp-content/uploads/2023/04/10-AMBULANCE-QUESTIONS-FINAL-VERSION.pdf
How do I stop someone choking on their vomit if they are already choking?
Put them into the recovery position. Call an ambulance. Monitor them for consciousness.
I think my friend is an alcoholic, he drinks at every single opportunity, what can I do to help him?
Talk to your friend gently, caring and supportively about their drinking to see what they think. Offer them your support and let them know there are plenty of services available if they want help with their drinking or other issues in their life.
See the "helplines and support" heading.
What if I’m a sober driver, driving my friend home, and they are unresponsive?
Safely pull over and call an ambulance if they are unresponsive and administer first aid. Make sure they are breathing, and their head is not forward obstructing airways. You can put them in the recovery position outside the car, somewhere safe.
If they can sit on their own, you can also keep them in the seat and watch their breathing, and make sure their head doesn't fall forward and suppress breathing.
What do you need to do if the emergency operator says that an ambulance will take some time to arrive, e.g. 30 mins or longer?
NSW ambulances will first send an ambulance to the most urgent cases. If your friend is deteriorating, you can call 000 again and let them know, and they will advise you what to do. You could also ask a responsible adult to drive your friend to the nearest emergency department.
Is it true that there isn’t a whole lot of negatives about cannabis outside of driving?
Smoking cannabis, like inhaling any smoke, is bad for your lungs, especially as most cannabis smokers in Australia mull/mix it with tobacco. Read more about the effects of cannabis smoking on the lungs here.
For some people cannabis can trigger a permanent mental illness (e.g. schizophrenia).
Many young people form a cannabis habit and can't go through their day without having a smoke.
Some people who use cannabis occasionally have little or no effect on their lives. Many young people who use cannabis regularly experience things like anxiety and loss of motivation.
Cannabis can affect brain development. It affects memory and attention, which affect your ability to take in and remember new information. This makes it hard to learn something new or doing complex tasks. If you use cannabis heavily, these problems don’t go away.
If you want to know more about how different drugs affect your brain go to this website.
Isn’t cannabis better for you because it’s natural and non-addictive?
Cannabis does affect your health in negative ways. Inhaling any smoke is bad for your health and cannabis smoke contains a lot of tar because it is oily. Most people smoke it mixed with tobacco so they get the negative effects of tobacco too. For some people cannabis will trigger unknown permanent lifelong mental illness.
Addiction and dependence can occur when using cannabis. It is called Cannabis Use Disorder. However, cannabis shows much lower dependency rates than other recreational drugs, such as alcohol and nicotine. Since most cannabis users mix it with tobacco, regular cannabis users are often nicotine dependent even if they do not consider themselves tobacco smokers.
Would you consider cannabis a 'gateway drug' to harder drugs?
The research is not clear about this question. There is an association between using cannabis and other illicit drugs, but it’s not clear if this is causation or correlation.
What's the difference between cannabis and cigarettes?
Cannabis and cigarettes are consumed differently (cannabis can be smoked through joints, pipes, or vaporising devices, ingested through food or drink, etc.).
Cannabis and tobacco contain different active ingredients. Cannabis smoke contains cannabinoids whereas tobacco smoke contains nicotine.
Most people smoke cannabis with tobacco, meaning you get the negative effects of both drugs. This website from the American Lung Association goes into how cannabis can affect your lung health.
Are joints better for you than ciggies?
Many joints contain both tobacco and cannabis, so you get the harmful effects of both types of smoke. Tobacco smoke contains up to 4000 harmful chemicals and like any smoke, isn't good for your lungs.
For cannabis-only joints, the smoke produced from burning cannabis has much higher levels of tar due to cannabis oil burning. It is quite damaging to the lungs. Joints often don't have filters except for the rolled cardboard type, so you might be inhaling in some big bits which can do damage to your airways.
An American article explores the impacts of marijuana smoking on the lungs. It includes references and links to further information about cannabis and its effects.
Can't cannabis be used for medical reasons?
Just because cannabis is used medicinally does not mean it is harmless or safe when used recreationally.
Most medicinal cannabis is high in CBD but not THC (does not get you stoned). It is prescribed for certain conditions, including epilepsy and cancer.
Some medicinal cannabis includes precise levels of cannabinoids (active compounds), including THC. This is prescribed by a doctor in controlled doses in Australia.
It is not the same as consuming unknown amounts of cannabis from uncontrolled sources advertised on the internet and social media.
Patients legally treated with medical cannabinoids are monitored for safety.
This factsheet from DARTA covers more on safety.
Why has it become a habit for me to smoke weed?
You can get physical and psychological dependence on cannabis. Dependence means that it takes up a lot of your thoughts, emotions and activities. It can lead to problems with health, money, relationships, and employment.
Another reason smoking weed becomes a habit is that most people mix their weed with tobacco. The nicotine in tobacco is highly addictive, so many weed smokers are actually nicotine dependent. It means that if you want to stop smoking weed you might have some nicotine withdrawal symptoms. Some people use nicotine replacement products like patches, lozenges and inhalers to help with stopping or reducing cannabis smoking.
There are many websites about cannabis addiction. The Australian Drug Foundation website and healthdirect website are the most reliable and relevant.
Is it possible to get stuck in a 'loop' from a high intake of marijuana?
It’s possible that people can have a bad ‘trip’ from cannabis. Particularly if they have an underlying mental condition or the cannabis strain is very potent.
Some teens who use cannabis trigger an underlying mental health illness. This is often permanent. They might have a mental health condition for the rest of their lives even if they never use cannabis again.
You’re more likely to have problems if you start using marijuana at an early age, or use it regularly. Regular cannabis users have higher levels of depression than those who do not use it.
Anyone can develop a tolerance to cannabis, meaning you need more of the drug to experience the same effects.
You can also get physical and psychological dependence on cannabis. Dependence on cannabis means that it takes up a lot of your thoughts, emotions and activities. It can lead to problems with health, money, relationships, and employment.
Another effect can be psychosis (seeing and hearing things that aren’t real). This is more likely to happen if the person has a pre-disposition to schizophrenia which can be triggered by cannabis use.
For more information on cannabis’ effects on mental health, see the Australian Drug Foundation, and Headspace.
Does cannabis have any long term negative effects on someone?
You’re more like to have problems if you start using marijuana at an early age, or use it regularly.
Regular cannabis users have higher levels of depression than those who do not use it.
Anyone can develop a tolerance to cannabis, meaning you need more of the drug to experience the same effects.
You can also get physical and psychological dependence on cannabis. Dependence on cannabis means that it takes up a lot of your thoughts, emotions and activities. It can lead to problems with health, money, relationships, and employment.
Another effect can be psychosis (seeing and hearing things that aren’t real). This is more likely to happen if the person has a pre-disposition to schizophrenia which can be triggered by cannabis use.
People who use marijuana over long periods can also:
• lose their sex drive
• have problems with memory
• have learning difficulties
• have mood swings
• think about suicide
• get chest infections and sore throats, asthma or bronchitis
• have lower sperm counts
• have irregular periods.
This website from Your Room and this one from healthdirect go into more detail on the long term effects.
Is it true that the use of weed can permanently affect your brain's ability to produce happy chemical like dopamine and serotonin?
Available evidence shows that regular long term THC exposure (from using weed) is linked with your brain reacting less strongly to dopamine (pleasure and reward chemical).
More research is likely to come out in the next few years.
If you've used cannabis once, how long does it stay in your system?
For a one time use, cannabis should leave your system after 12 hours or so. However, this will vary depending on the dose, potency, person taking it etc. See the Cannabis Support and Information blog.
When you use weed, it is stored in your fatty tissue and released slowly into your bloodstream before you get rid of it from your body. The length of time it stays in your system depends on a lot of things. In general, it may be found in urine for 1 to 5 days after occasional use and up to 6 weeks if you’re a regular, long-term user.
Roadside drug tests in NSW only test for the presence of cannabis in your system – not intoxication. Long time or regular cannabis users can fail roadside drug tests even if they haven’t smoked for days before it.
For further information about roadside drug tests and cannabis, see the Australian Drug Foundation website.
It’s important to recognise that roadside drug tests in NSW only test for the presence of cannabis in your system – not intoxication – so long time or regular cannabis users can fail roadside drug tests even if they haven’t smoked for days before it.
For further information about roadside drug tests and cannabis, see the Australian Drug Foundation website.
What would happen if I took weed while having an underlying paranoia disorder?
Cannabis can trigger a psychotic disorder like schizophrenia in people who are already at risk of developing the disorder. In these people, using cannabis may mean they develop the problem earlier.
There is also some evidence that cannabis can produce psychotic symptoms in people with a family history of mental illness. It can also make existing psychotic symptoms worse and harder to treat.
Anyone who has an existing mental health issue or who has a close family member with depression, psychosis, bipolar disorder or anxiety should avoid cannabis. They are at high risk of mental health problems being triggered by the drug.
Healthdirect has more information on this topic.

What can cannabis do to people with ADHD?
Some people with ADHD are self-medicating with cannabis and reporting its effects. Some think it is helpful to treat their ADHD. However, there is not much scientific evidence about this, especially about young people with ADHD.
Can you have hallucinations from weed or experience psychosis while on weed ?
High doses of cannabis can cause hallucinations, although cannabis isn’t categorised as a hallucinogen. Its effects can vary from person to person. Different strains and types of weed can produce different effects.
As a result, weed can be classified as a depressant, stimulant, or hallucinogen.
Hallucinating while stoned may be influenced by an underlying mental health condition. For it to be classified as psychosis it has to last longer than the duration of the trip. Unfortunately, sometimes psychosis triggered by cannabis use is permanent.
It is hard to know during hallucinating on cannabis whether it's the trip or you're going to have long term psychosis. This uncertainty can cause people to feel very anxious during intoxication and cause a 'bad trip'.
For more information on cannabis mental effects, including paranoia and hallucinations, see this Guardian article. It was written by researchers at the University of Oxford, the Institute of Psychiatry at King's College London, and the University of Manchester.
Can you get addicted from spun weed?
It’s highly likely that cannabis mixed with tobacco can lead to nicotine addiction, although cannabis can be addictive as well.
You can get physical and psychological dependence on cannabis. Dependence on cannabis means that it takes up a lot of your thoughts, emotions and activities. It can lead to problems with health, money, relationships, and employment.
As well as the risk of cannabis dependence, many people mix their weed with tobacco. The nicotine in tobacco is highly addictive, so many weed smokers are actually nicotine dependent. It means that if you want to stop smoking weed you might have some nicotine withdrawal symptoms. Some people use nicotine replacement products like patches, lozenges and inhalers to help with stopping or reducing cannabis smoking.
There are many websites about cannabis addiction. The Australian Drug Foundation website and healthdirect website are the most reliable and relevant.
If someone has like 0% body fat will cannabis stay in them for as long?
No one has 0% body fat. When you use weed, it is stored in your fatty tissue and released slowly into your bloodstream before you get rid of it from your body. The length of time it stays in your system depends on a lot of things. In general, it may be found in urine for 1 to 5 days after occasional use and up to 6 weeks if you’re a regular, long-term user. This website about cannabis has more information.
Are cannabis 'edibles' safer than smoking?
The effect of eating cannabis takes a lot longer than smoking cannabis. This is because it has to be absorbed into your blood through your liver. It can take between 1 and 3 hours to feel the full effects.
Because of this delay, users often end up eating more cannabis because they think it isn’t working. This is more likely if you’re new to eating cannabis. This can lead to overconsumption, which can lead to severe anxiety, panic attacks, nausea, and in more extreme cases, delirium or psychosis (see question and answer regarding getting caught in a loop, or having a ‘bad trip’ on cannabis).
If you also have alcohol or medications in your system, your body may process cannabis differently. This could lead to higher levels in your blood. This could cause you to ‘green out’ or ‘white out’ (feeling sick after consuming cannabis).
In a green out you go pale (turning green or white) and start to sweat. You feel dizzy and nauseous, and may vomit. There are cases of people becoming very sick after eating high levels of THC. Whilst a trip to an emergency department for cannabis is not very common, if it happens it is often due to someone having eaten it.
No matter how cannabis is used, it can be highly problematic for some people. Studies have found that cannabis can negatively impact mental health.
This DARTA factsheet has more information about edibles:
Are bongs better for you than joints?
It's hard to say. Bongs might be a smoother toke as it eliminates the dry heat you get from a joint but the effect can be deceiving as the smoke from a bong is still filling up your lungs. Bong safety research has not been super high on the list of medical research priorities so we don’t really know!
My girlfriend had anger issues and she started to use marijuana on a daily basis and it has calmed her down. Is this normal?
Cannabis can ‘chill’ people as it has some relaxing and slowing down effect on some people. However, it may be more useful for your girlfriend to seek help to deal with her issues in a healthier way than self-medicating.
Surely if cannabis is being legalised more and more, there must be a reason for it? Is it not really that bad?
Cannabis possession has not been decriminalised nor legalised in NSW. See below question about the difference between decriminalising and legalising cannabis.
In NSW doctors are able to prescribe cannabis to treat symptoms for particular conditions (e.g. Cancer, epilepsy, chronic pain, insomnia etc.).
The question is probably more to do with the safety of being on cannabis while driving. We can think about it in a similar way to alcohol – while alcohol is legal, it is unsafe (and illegal) to be intoxicated while driving.
A lot of research shows that marijuana makes your judgment, motor coordination, and reaction time worse. This leads to impaired driving ability.
People that have been in car crashes have their blood tested for drugs. The illegal drug found most often in people’s system is cannabis.
What is the difference between ‘decriminalised’ and ‘legalised’?
ACT, SA, NT have decriminalised minor cannabis offences. This includes the possession of a small amount of the drug for personal use.
This means that people found with a small amount of cannabis can get a “civil penalty”, like a fine, instead of a criminal charge. It’s like getting caught for speeding and getting a fine.
“If an offence is decriminalised, it does not mean that it is legal. Legalisation of cannabis would mean that cannabis would no longer be an illicit drug, but would be a legal drug like alcohol and tobacco.”
This website about cannabis goes into this in more detail.
In terms of the consequences, this government website says “In NSW, first time offenders caught carrying a small amount of cannabis may be issued with a formal caution, which can include information about the harms associated with cannabis use and a number to call for drug related information or referral. A person can only receive up to two cautions.”
But did Canberra legalise weed?
Cannabis is not legalised in the ACT but decriminalised. This means people who possess or use small amounts of cannabis won’t be penalised.
It is still illegal to drive in the ACT with cannabis in your system. See this government website for more detail on the rules in the ACT.
Is weed classed as a hallucinogenic drug as you may experience hallucinogenic affects and your senses being affected? Is this the reason for it being illegal?
Historically, cannabis was considered a hallucinogenic drug because of its psychoactive effects. However, the types of hallucinatory experiences that people have on cannabis are quite different to 'classic' hallucinogenic drugs. Its pharmacology (what effects it has on the body) is also different to hallucinogenic drugs.
Hallucinations on weed are possible but are not common.
What is the chance of weed being laced with something else?
It’s hard to know what the chances are that weed will be laced. Some people believe lacing could be common in illicit cannabis (as opposed to regulated medicinal cannabis) as it can add weight to the product or change how it affects the user.
Some media reports in recent years are about people who have had weed that was likely laced with something else. This includes methamphetamine (‘ice’) or other drugs, or toxic chemicals like rat poison and insecticides. These articles from the Courier, the ABC and the Herald are examples of these reports.
If you’re around someone who has smoked cannabis, how do you get it out of your hair?
Shampoo your hair.
Hair analysis/testing is not a method routinely used in Australia by police forces, but cannabis can be detected in hair samples depending on the amount of cannabis smoked. This study indicates that regular heavier use is more likely to be detected in hair samples.
How far away do you move from a person smoking cannabis to avoid getting the smell on you? And what if you can't? (E.g. In a small room with the smoker)
If you're in the same room as someone smoking cannabis, it will be very difficult to avoid their smoke smell on you. You should suggest to them that they go outside to smoke or you should leave or ventilate the room. Smoke smell can stay on clothes or hair until washed so avoid being around smokers if you dislike it.
You are likely to get some smell on cloths and hair and may be picked up for testing, but you’d be unlikely to fail a roadside drug test.
For details about passive cannabis smoking check out this article, but note that this study was done in an unventilated room with high THC cannabis smoke.
How would you help a pet that you accidentally got stoned?
Cats and dogs can become intoxicated by cannabis by inhaling second-hand smoke, eating edibles (e.g. baked goods containing cannabis), or eating cannabis directly. Most exposures are accidental.
The effects of cannabis on your pets are more dramatic and potentially more toxic when compared to humans. A small amount of cannabis is all it takes to cause toxicity in cats and dogs. A small amount may affect one pet more than another, so there is no official safe level of exposure.
If you notice unusual behaviour in your cat or dog and think they may have been exposed to cannabis, take them to your vet or the nearest emergency vet hospital.
VCA Hospitals, an American based veterinary hospital group, provides further information in this article.
What happens when someone becomes abusive while on weed?
Weed or cannabis does not usually make people abusive, unless combined with other drugs like alcohol or ice.
People intoxicated by cannabis may not want company or to be looked after. It is probably best to monitor their condition from a distance and/or alert others. The person may have other underlying health conditions which are affected by the cannabis use.
Your first priority must always be your personal safety – never put yourself in a situation where you could get hurt. If your friend does not want your help, involve someone else, try to work as a team and if you are really worried about their safety, call 000.
What can I do to get away from parents that smoke pot?
If you have parents who are smoking cannabis and it affects you, consider talking to them about the impacts on you and how you feel about it. Also consider seeking counselling, perhaps with your parents. There may be ways that your parents can minimise their cannabis smoking or its impacts on you. This website has information about drugs, as well as phone numbers and links to support services.
What do you do if your friend is greening out?
Support your friend. Make sure they are in a safe, quiet location. Provide them with water to sip. Put them in the recovery position if they start vomiting. Seek medical help (ambulance 000) if they become incoherent or unconscious.
For more information see this poster https://darta-digital-cards.pages.dev/greening-out
If I eat a lot of bud, will it still make me high?
Generally you can’t get high from eating raw cannabis, as the THC needs to be activated by heat (cooked, burned) to have an effect.
In terms of eating cooked cannabis (‘edibles’ such as cookies, brownies, cakes etc.) it will depend on the quantity and quality of the cannabis used in making the edible. As cannabis buds have the highest concentration of THC of all the plant parts you could get very high.
With eating cannabis, it is better to wait for at least an hour as the effect takes much longer to occur. Many people eat more when they don't feel anything after 30 or 40 minutes. Then when it hits them it can be a far stronger high than they expected.
Do bongs get you more high than joints?
There are probably a few reasons why people say they feel higher using bongs compared with joints. When smoking a joint some of the smoke gets lost into the air as the cigarette is lit. With the bong much of the smoke is getting inhaled into your lungs. You may also feel the effect quicker because you inhale deeper on the bong.
If I liquify marijuana, then use it intravenously, will the affects be the same?
People who tried it got very sick (vomiting, heart problems). When done as part of a controlled study, people who received pure THC intravenously suffered psychotic side effects similar to schizophrenia, as well as anxiety. Not a good idea obviously.
Is it true that abuse of MDMA can lead to permanent damage to a person’s ability to produce serotonin?
Yes, it is true. People who use MDMA regularly can get long term effects. These include trouble controlling their emotions, problems with memory and concentration, personality changes and depression (linked to reduced serotonin levels in the brain).
The Victorian Better Health Channel provides an overview of the effects of MDMA and possible long term impacts on serotonin.
What are your thoughts on MDMA- assisted psychotherapy?
There is emerging evidence that MDMA-assisted psychotherapy might be helpful when done by well trained and qualified therapists for certain conditions, like post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) or end of life support.
However, just like medicinal cannabis, the MDMA used in laboratories for clinical trials is made very ‘pure’ and monitored for safety. Drugs you buy off the street may contain other dangerous ingredients.
MDMA known as “Molly” or “Ecstasy” are types of street substances which often contain other dangerous ingredients and may or may not contain MDMA. In clinical trials, pure, laboratory grade MDMA is used in limited frequency and in moderate doses and is taken under medical supervision.
What are the long term effects of MDMA?
Long term effects of MDMA can be:
- Depression
- Anxiety
- Memory loss
- Kidney failure
- Haemorrhaging (internal bleeding)
- Psychosis
- Heart issues
- Convulsions
- Death.
Other concerns are:
- Long-lasting brain damage affecting thought and memory
- Damage to portions of the brain that regulate learning, sleep and emotion.
- Damage to nerves.
The Australian Drug Foundation and healthdirect websites provide a detailed outline of the long term effects of MDMA.
What’s in caps?
'Caps’ can relate to drugs that are sold as a pill or capsule. It can be anything! But it is usually a vessel for: MDMA/ecstasy or magic mushrooms.
How many grams of MDMA is normally in a cap?
It’s impossible to say how much MDMA is normally in a cap, as pills/caps are nearly always cut with other substances. Some research suggests MDMA content of caps ranged from 0 to 245 mg per cap. However, the bigger risk is of pills/caps being mixed/contaminated by other more dangerous substances or not containing MDMA at all.
Is cocaine illegal?
Yes, it is illegal in all Australian states and territories.
Can you die from crack?
Yes, some crack users can overdose and die. You can read more about cocaine overdose on Your Room
What happens if you eat a large amount of cocaine?
Cocaine can have serious side effects whichever way it is taken. Eating cocaine poses health risks including:
- heart attack
- high blood pressure
- anxiety
- poor decision-making
- lack of self-awareness
- irritability
- panic
- paranoia
- tremors
- dizziness
- increased energy and alertness
- restlessness
- sweating
- coma
Cocaine is particularly susceptible to being 'cut' (contaminated) with other chemicals which can also be very dangerous. The Your Room webpage about cocaine has more information.
How long does it take to overdose on cocaine?
It depends on how much you are taking and how quickly, as well as how you react to the drug. Overdose of cocaine is more likely to occur in people with pre-existing heart conditions or who are older. Even small amounts may cause overdose with some people who have an especially strong reaction to it. It's hard to know who is going to have these reactions.
Why is heroin illegal?
Heroin is illegal because it can be dangerous to a user’s health and life (and the lives of others).
There are harms associated with heroin use. Long-term effects of heroin include:
- Severe constipation
- Tooth decay (from lack of saliva)
- Irregular menstrual periods in females
- Impotence in males
- Loss of appetite and weight
- Neurochemical changes in the brain
- Memory problems
- Mental health issues including depression
- Physical dependence and associated withdrawal, which give you flu-like symptoms
- Harms associated with regular injecting
You can see more data about illicit opioid use and drug laws in Australia on these sites.
Is heroin good for you if the environment is good?
Heroin is illegal because it can be dangerous to a user’s health and life (and the lives of others). See the question above for a list of potential harms. Most will occur even if you took heroin in a relatively safe environment.
How do I hide my heroin use from my friends?
Hiding drug use can be a sign you have a drug problem. It can be harmful to your relationships and affect your support network.
If you don’t want to talk to your friends, see a doctor or call a support service.
Whether you are having issues with alcohol or other drugs, are concerned about someone else’s alcohol or other drug use, or just have general questions, you can call ADIS. Call them any time of the day or week for support, information, counselling and referral to services in NSW. This page has more information about getting help.
What are nangs?
‘Nanging’ is breathing in nitrous from small, pressurised canisters (bulbs) like the canisters used for whipping cream.
Some of the harms associated with nanging include:
- injuries related to inhaling the gas
- accidents and falls
- asphyxiation (suffocation)
- nerve damage
Be careful, the cooking grade nitrous (NO2) is not quality controlled like the medical grade. You can't be sure what's in the cartridge. It could contain dangerous Carbon dioxide (CO2), which looks the same, but can kill or cause brain damage if inhaled!
How many nangs is too many?
There is no safe level of drug use. Use of any drug always carries risk. Nitrous oxide affects everyone differently, based on: the amount taken, the user’s size, weight and health, whether the person is used to taking it, whether other drugs are taken around the same time.
Whilst the risk of overdose from nitrous oxide is low, people with heart conditions or abnormal blood pressure may be at higher risk. This is because the drop in oxygen levels caused by inhaling the gas raises the heart rate, which could cause problems.
The Alcohol and Drug Foundation details the risks of nangs. The gas from the bulbs is intensely cold (-40C degrees) and can cause frostbite to the nose, lips and throat (including vocal cords).
As the gas is also under constant pressure, it can cause ruptures in lung tissue if inhaled from the bulbs. Releasing the nitrous oxide into a balloon helps to warm the gas and normalise the pressure before inhaling.
Faulty gas dispensers may also explode and cause injury. Dispensing multiple gas canisters with one cracker (a handheld device used to 'crack' a nitrous oxide bulb/whippet) can also cause cold burns to the hands.
Check out this link about nitrous oxide for more information.
This DARTA facsheet has more information:
Is Ketamine safe? How can someone safely use Ketamine?
Ketamine is used as an anaesthetic (pain medication in medical procedures) for humans and a tranquilizer for animals. It is sometimes used illegally by people to get high.
It can produce psychedelic effects, causing a person to see, hear, smell, feel or taste things that aren’t really there.
Ketamine can cause:
- feeling relaxed
- feeling detached from your body (‘falling into a k-hole’)
- hallucinations
- confusion and clumsiness
- increased heart rate and blood pressure
- slurred speech
- blurred vision
- anxiety
- panic and violence
- vomiting
- lowered sensitivity to pain.
If you take a large amount, it can cause:
- not being able to move
- rigid muscles
- high body temperature
- fast heartbeat
- convulsions
- coma and ‘near death’ experiences
You can learn more about Ketamine here.
If I were to have ket the day before my blood donation will it affect the patient receiving my blood?
You wouldn't be allowed to make the blood donation in the first place. The Australian Red Cross doesn't accept blood from anyone under the influence of drugs. Being intoxicated affects your ability to understand and answer the donor questionnaire and declaration. It also affects your body’s ability to tolerate blood being taken.
Ketamine can be used in different forms, including injecting intramuscularly (into the muscles). If you’ve injected drugs which weren’t prescribed by a registered medical practitioner (like a GP or specialist doctors), you’ll need to wait 5 years before you can donate blood.
How long does ice stay in your system?
The “high”of ice can last for up to 12 hours, depending on how much you take, how strong it is, your body size, if mixing with other drugs and if you’ve had it before. The ‘come down’ can take a few days.
If you regularly use high doses of ice, it can cause ‘ice psychosis’ which can last a few days.
This factsheet from DARTA about how long drugs stay in your system says that amphetamines can stay in your system for 2 to 4 days.
Ice is very addictive and it can be very hard to stop using it if you are a regular user.
Will prescription amphetamines i.e. Vyvanse or Ritalin give a positive result in a drug test?
The saliva tests used for MBTs don’t detect ADHD medications. They don’t detect the presence of prescription drugs or common over-the-counter medications. This website has more information.
Is it true that people on ice have super strength?
Ice can produce short-term effects like increased energy, confidence and aggression. This can differ from person to person.
The effects are temporary. The ‘come down’ from ice can make people feel the opposite way, i.e. exhausted, feeling down or low, irritable, agitated and paranoid.
See this site for more about how ice affects the body.
What are the effects short term and long term of hallucinogens e.g. Mushrooms, LSD and DMT?
The effects of hallucinogens depend on a few things like the type of drug, the strength of the dose, and the user’s state of mind.
The effects of hallucinogens can be immediate or long term, you can find a list of short and long term side effects on the Positive Choices site.
What is the government’s stance on psychedelic therapy, Will we seen any of this in the future?
A recent review found that psychedelic drugs show promise to treat complex mental health illness that have been resistant to other treatments. This is only if used in closely supervised clinical settings with intensive professional support. This review was written by the TGA (Therapeutic Goods Administration), part of the Australian Government Department of Health.
The TGA decided in December 2021 to leave these drugs as schedule 9 (prohibited) drugs until more data and evidence becomes available. When/if this occurs, the TGA might change these drugs’ status to schedule 8 (controlled) drugs. This would enable their broader use under medical and psychological supervision to treat complex mental health conditions.
Director of psychedelic research at Edith Cowan University's school of medical and health sciences, Dr Stephen Bright, believes that it may be a while before these drugs can be used medically. He strongly advises against self-medication.
You can read this ABC article about use of MDMA and magic mushrooms to treat mental illness in Australia.
How dangerous is LSD/acid?
The Alcohol and Drug Foundation has information about how LSD can affect everyone differently, based on:
- size
- weight
- health
- whether the person is used to taking it
- whether other drugs are taken around the same time
- the amount taken
- the strength of the drug (varies from batch to batch)
- the person’s state of mind
If you take a large amount, the negative effects of LSD are more likely to happen. Call an ambulance straight away (000) if you or a friend have any of these symptoms:
- Panic
- Paranoia
- increased risk taking
Ambulance officers don’t need to involve the police.
Sometimes you can experience a ‘bad trip’ involving a disturbing hallucination. This can lead to panic and risky behaviour, like running across a road or attempting self-harm.
More information on hallucinogens is here.
Can you get stuck in a trip from mushies or LSD?
The Victorian Health website about hallucinogens states that: "Some people may experience ‘flashbacks’, which can happen days, weeks, months or even years after taking the drug. They briefly relive the hallucinations of a previous trip so powerfully that it seems as if they have been transported back in time and space, or they may experience distortions of their present reality. "
There are some incidents when a bad trip triggers a permanent mental health illness like schizophrenia. You cannot know in advance to whom it might happen.
What is the government’s stance on psychedelic therapy? Will we see any of this in the future?
A recent review found that psychedelic drugs show promise to treat complex mental health illnesses that have been resistant to other treatments. This is only if used in closely supervised clinical settings with intensive professional support. This review was written by the TGA (Therapeutic Goods Administration), part of the Australian Government Department of Health.
Since 1 July 2023, psychiatrists can be authorised to prescribe products containing 3,4‑methylenedioxy‑methamphetamine (MDMA) or psilocybin for use in psychedelic-assisted psychotherapy to treat specific mental health conditions.
MDMA may be prescribed for the treatment of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Psilocybin may be prescribed for treatment-resistant depression (TRD). For these specific uses, psilocybin and MDMA have been listed as Schedule 8 (Controlled Drugs) medicines in the Poisons Standard.
To be able to prescribe MDMA or psilocybin for these conditions, a psychiatrist must be an Authorised Prescriber (AP) under the TGA’s Authorised Prescriber scheme- external site
Before patients for whom approved medicines are not effective can receive MDMA or psilocybin treatment, psychiatrists must carefully assess whether the benefits are expected to outweigh the risks in those patients.
Director of psychedelic research at Edith Cowan University's School of Medical and Health Sciences, Dr Stephen Bright, believes that it may be a while before these drugs can be used medically. He strongly advises against self-medication.
You can read this ABC article about use of MDMA and magic mushrooms to treat mental illness in Australia.
I have had terrible experiences with drugs and didn't tell anyone because I didn't want to get in trouble with the law. What should I do?
You have some anonymous support options available to you. Your first port of call could be the Alcohol & Drug Information Service (ADIS) NSW. This is a 24/7 toll free anonymous helpline to support people who are having problems with alcohol and/or drug use. The number is 1800 250 015. You can also find more information about getting help here- including the web chat service.
How can you help people to quit and understand that it’s dangerous?
We can't always make others do what we want. What you can do is help them find the facts and let them know that you care about them and are there for them. This website has information about drugs, as well as phone numbers and links to support services. These services have trained professionals to help people that want to stop using drugs.
For example, whether you are having issues with alcohol or other drugs, are concerned about someone else’s alcohol or other drug use, or just have general questions about alcohol or other drugs, you can call ADIS. Call at any time of the day or week for support, information, counselling and referral to services in NSW.
See this factsheet DARTA about what do when worried about a friend for more information.
How can you help someone who does drugs to get better?
It would be worthwhile seeking counselling, talking to a teacher or parent, and reaching out to see what options are available to help them with their problem.
Many teens use drugs occasionally and go on to live very functional and successful lives. But if you think your friend’s drug use is problematic, hearing it from someone close might be a much needed wake up call for them. If your friend has a drug problem, try talking to them about it and asking them whether they want to get help.
There are lots of services available (including your doctor and school counsellor) who can help with getting off drugs, but the person who is using drugs needs to recognise that it’s a problem for him/her. Drug abuse may be a symptom of underlying issues causing stress and there are other ways to deal with life's pressures.
This fact sheet has more information about what to do when worried about a friend.
See also answer to question above.
Can you unlock mental illness after very few uses?
Yes, unfortunately you can. Some drugs, particularly hallucinogens, can trigger underlying mental conditions, for example psychosis. As drugs effect people differently, you can't be certain how a drug might affect you. The best way to avoid triggering any underlying mental illness is to avoid taking drugs. This website has an A-Z of drugs and their effects.
Can drugs cause depression?
Beyond Blue writes: "If you’re going through a tough time, it can be tempting to use drugs and alcohol as a coping strategy. However, these are addictive substances that can cause symptoms of depression and/or anxiety or make an existing problem worse, while making recovery much harder. Some people with depression and/or anxiety can also develop problems with drugs and alcohol, which may also need treatment."
Does the no bread rule apply for drugs as well?
This question is in relation to Paul Dillon’s warning not to give drunk people bread to eat as they could choke on partly chewed bread. It can also be dangerous to have partly chewed bread when dosing off when using other drugs as it could choke you.
Bread doesn’t sober or straighten you up. If you see someone who is very drunk and/or stoned who is eating while drifting or dosing, watch their breathing very carefully, place them in the recovery position and clear their airway if you suspect they are choking. Call for help if they seem to have lost consciousness or if you need help with looking after them.
Can you get high off of nutmeg?
The chemical responsible for the “high” caused by nutmeg is known as myristicin. Myristicin is found naturally in plants such as parsley, dill, and nutmeg.
While nutmeg may seem like an easy way to get high, myristicin is a potent and dangerous compound when taken in large amounts. Toxic doses of myristicin have caused organ failure in some people. People have died when myristicin is used in combination with other drugs.
What is the most dangerous drug you can take?
It depends what we mean by 'dangerous'. Dangerous could mean: which drug causes the most road accidents, or the most serious health consequences, or the most hospitalisations or the most deaths. And then there are also other dangers to consider, like the drugs that have the most harmful impacts on crime, the environment, or society in general.
With that said, a 2019 Australian study found that alcohol is the most harmful substance when taking into account harms to self and others. Fentanyls were considered the most harmful to users.
If I intravenously use drugs, will it generate a stronger affect?
Using drugs intravenously (injecting into a vein) means a greater amount of the drug will get into your bloodstream in a shorter space of time.
This information about drug administration routes says “Intravenous (IV) drug abuse may be the quickest way to get high since the drug is placed directly in the bloodstream with injection.
Shooting drugs is also considered one of the most dangerous methods of drug use since it can quickly lead to addiction and accidental overdose with the added risk of getting infected from reused syringes.
Not all drugs can be taken intravenously.”
What drug do u suggest for a decent night out but not dangerous to your body?
We don’t recommend drugs for a night out. If you choose friends and places/events to attend that are fun you'll be high on life :)
Can't alcohol unlock mental illness as well?
Any drug, including alcohol, has the potential to impact on mental health, particularly if it is abused or overused. If you have concerns about an underlying mental illness, it is best to avoid drugs and alcohol and talk with a health professional about your concerns and how drugs or alcohol may affect you.
Can you have drug transfer similar to the alcohol transfer (from snogging) you spoke about yesterday?
Yes, it is possible for drug traces to pass through saliva. This story is about a Canadian athlete who tested positive to cocaine, there is also a medical case study of a woman who developed an allergic reaction to a drug taken by her husband after kissing.
What if a friend hasn't been the same since a trip?
Check in with your friend to see if they're OK and if they're not, help them find support from a counsellor or medical professional. You might want to point out to them that their behaviour has changed since that trip. Drugs affect everyone differently and may trigger underlying mental health conditions. You can also find more information about getting help here.
Can I get high from inhaling the exhaust of my car?
Exhaust fumes are extremely dangerous and can seriously injure and even kill people who are exposed.
Carbon monoxide (CO) is produced by internal combustion engines (e.g. cars, motorbikes, trucks, forklifts etc.). If you breathe in a lot of it, it can cause CO poisoning. It displaces oxygen in the blood and deprives the heart, brain and other vital organs of oxygen.
Large amounts of CO can overcome you in minutes without warning — causing you to lose consciousness and suffocate.
If you think you or someone else has CO poisoning, get away from the source of CO and immediately call 000.
If I sniff petrol out of a car will it make me dizzy?
Yes, dizziness is one of the common effects. Sniffing petrol usually causes euphoria, dizziness, numbness and giddiness, and can lead to hallucinations, slurred speech and nausea.
Petrol sniffing is dangerous and can have long term impacts on your health. The poisonous chemicals in petrol gradually damage the brain, heart, lungs, immune system, liver and kidneys. The longer a person sniffs, the worse they damage these organs. You should avoid breathing any petrol vapours!
This fact file about petrol sniffing has more information.
What drugs from a pharmacy are most harmful when mixed with alcohol?
As a general rule, combining drugs or medications (prescribed or not prescribed) with alcohol is not a good idea. The effects can be unpredictable.
Alcohol can affect how well medications work or make you feel sick if you’re on certain medications.
A single alcoholic drink with some medications can cause drowsiness or dizziness. This is dangerous for travel, especially when driving, crossing roads on foot or by bicycle. It may be difficult to concentrate on school or other work.
Some medications increase how easily you get drunk.
Drinking alcohol with more than one kind of medication means you’re more likely to:
•increase the effects of alcohol
•decrease how well the medication works for you.
If you’re not sure, talk to your pharmacist or doctor. You can also look for information that comes with your medication.
This fact sheet contains commonly used medicines that interact with alcohol and their possible reactions.
You can also look over this very detailed American fact sheet. Note that some of the medication brand names are specific to the US market.
Explain the logic behind the saying "Cone before beer, you’re in the clear. Beer before cone, you're on your own"
Once alcohol is in your system, it boosts the effects of marijuana. It opens up your blood vessels, allowing more THC to be absorbed.
It’s worth remembering that each person reacts to alcohol and to marijuana (and to combined alcohol and marijuana use) differently. The effects of weed alone can be unpredictable depending on the type of cannabis you’re taking, your mental state and your family history. Mixing marijuana with other drugs can increase your risk and land you on your backside greening out or worse!
What are the effects of mixing alcohol with psychedelics (like (LSD or magic mushrooms)?
The effects of mixing psychedelic drugs and alcohol are often unpredictable. The main risks are that you might perceive the effects of alcohol to be lowered. This increases your risk of drinking too much and making you more vulnerable to a nasty hangover or alcohol poisoning.
Mixing psychedelics and alcohol could also have an impact on your mental wellbeing. If you are already in a negative space, psychedelics combined with alcohol could make you feel even more down.
What drugs from a pharmacy are most harmful when mixed with alcohol?
Problems can happen with many different medicines. The most common ones are:
- antibiotics
- antidepressants
- painkillers
- sleeping tablets
- certain antihistamines used in cough and cold, travel and allergy medicines.
If you take the wrong medicine with alcohol, you can get:
- nausea and vomiting
- headaches
- sleepiness
- dizziness and fainting
- blood pressure changes
- uncharacteristic behaviour
- poor or loss of coordination
- accidents
It can take time for your body to process alcohol and medicines. You can have these symptoms even if you don’t take the medicine at exactly the same time as drinking alcohol.
There is a risk of serious complications such as:
- liver damage
- heart problems
- internal bleeding
- weakened breathing
- depression
Combining alcohol and medicine can make it dangerous to operate machinery, drive or do physical activity.
This fact sheet contains commonly used medicines that interact with alcohol and their possible reactions.
The (American) National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism has a very detailed factsheet about alcohol and drug interactions. Note that some of the medication brand names are specific to the US market.
Is it true that you should never mix your drinks? ‘Liquor before beer, never fear. Beer before liquor never sicker’ - is this true? What does mixing drinks do?
Some people believe that mixing different types of alcoholic drinks will give you a worse hangover the next day.
However, as we drink more, we tend to start drinking faster. So, mixing drinks might not be a good idea as it:
- means it’s harder to keep track of how many drinks you’ve had, and
- increases how much alcohol you drink if you move from a beverage with a low alcohol content (like beer) to one with a higher alcohol content (like wine or spirits).
If I drink a lot of alcohol then use cocaine will it counteract the effects of alcohol and make me feel sober as cocaine is a stimulant and alcohol is a depressant?
Both alcohol and cocaine are strong acting drugs. You might feel sober, but you are definitely not. It is actually a very risky thing to do as mixing alcohol and cocaine increases the toxic effects.
Using cocaine with alcohol creates new chemicals. One of the most powerful of these metabolites is called cocaethylene. This product is stronger than either cocaine or alcohol alone. It increases toxicity to the heart, liver, and other major organs.
If you are on a medication, say an adhd stimulant, is drinking alcohol dangerous?
Alcohol is also known to increase some symptoms of ADHD, including inattentiveness, impulsivity, and lack of proper decision-making. Additionally, there could be a link between insomnia, those with ADHD and alcohol consumption. Insomnia causes difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep.
Alcohol actually changes the way your body processes it. This can lead to increased side effects, such as:
- racing heart rate
- high blood pressure
- trouble sleeping
Using both substances also puts you at an increased risk of alcohol poisoning and overdose. Over time, both substances can put a strain on your heart, increasing your risk of heart attack and stroke.
You should avoid drinking alcohol or using medicine that contains alcohol while taking ADHD stimulant medications. Stimulant drugs (like Adderall, Ritalin, or Vyvanse) or central alpha agonists (Kapvay, Intuniv) used to treat ADHD can interact with alcohol and may cause side effects like dizziness, drowsiness, heart problems or impaired concentration.
What drugs from a pharmacy are most harmful when mixed with alcohol?
As a general rule, combining drugs or medications (prescribed or not prescribed) with alcohol is not a good idea. The effects can be unpredictable.
Problems can happen with many different medicines. The most common ones are:
- antibiotics
- antidepressants
- painkillers
- sleeping tablets
- certain antihistamines used in cough and cold, travel and allergy medicines.
Mixing alcohol with medicines or other drugs can be harmful and may lead to an overdose.
Alcohol and some medications can make you tired, drowsy, or lightheaded. When mixing alcohol and medication the effects can be intensified.
Mixing alcohol with illegal drugs can have various effects depending on the type of drug.
If you take the wrong medicine with alcohol, you can get:
- nausea and vomiting
- headaches
- sleepiness
- dizziness and fainting
- blood pressure changes
- uncharacteristic behaviour
- poor or loss of coordination
- accidents
It can take time for your body to process alcohol and medicines. You can have these symptoms even if you don’t take the medicine at exactly the same time as drinking alcohol.
This fact sheet contains commonly used medicines that interact with alcohol and their possible reactions.
What are some of the risks associated with experimenting with drugs and alcohol at a young age?
Younger ages such as teenagers are particularly susceptible to the effects of drugs and alcohol as their bodies are still growing, with lots of changes going on in the brain and hormones. Starting drugs earlier in life can impact your mental health and physical health in bad ways, leading to addiction, dependence, side effects and long-term damage.
Understanding young people’s alcohol and drug use - Alcohol and Drug Foundation
What drugs are okay to mix?
No drugs are good to mix as they all affect people differently, depending on the person's chemistry, underlying health conditions, dose etc. Mixing drugs can have dangerous side effects. Mixing prescription medications with illegal drugs and/or alcohol can also be dangerous.
If I mix two different stimulants or two different depressants, will it give me adverse effects?
Yes, mixing two stimulants or two depressants can and is likely to produce more adverse effects.
The Alcohol and Drug Foundation describes mixing drugs in more detail. The effects of using one drug can be unpredictable for each person. Having multiple different drugs is even more unpredictable.
Taking two or more drugs from the same class (e.g. two depressants or two stimulants) increases the effects on the brain and body and increases the chance of an overdose. If you mix different classes of drugs, the effects are even more complicated and dangerous.
Mixing depressants can intensify effects like slowed brain activity and breathing rate. It increases the risk of injuries, vomiting, blackouts, unconsciousness and death.
Mixing stimulants, such as ecstasy and cocaine, can increase the user’s high, but also their risk of heart attack. It also increases the risk of psychosis, anxiety or panic attacks, as well as serotonin syndrome (a potentially fatal drug reaction).
The greatest risk of combined drug intoxication is death. 59% of unintentional drug overdoses involved multiple drug use.
Some of the side effects of combining drugs include:
- brain damage
- coma
- heart problems
- seizures
- stomach bleeding
- liver damage and failure
- heatstroke
- supressed breathing
- respiratory failure.
The Australian Government Department of Health's resource on polydrug use provides more information on the effects of mixing drugs.
What's the penalty for not wearing a seatbelt?
As of 1 July 2024, mobile phone detection cameras in NSW began enforcing seatbelt laws following legislation that was passed on 29 November 2023. Penalties start from $387 and three demerit points and double demerits apply.
Moreover, passengers aged over 16 can face fines for not wearing seatbelts, as well as for any instance of protruding body parts outside the vehicle during travel.
Search offences and penalties | NSW Government
What’s the limit on passengers for P platers?
The RMS Road Users Handbook details the rules on page 20. It states that for learner and provisional licence holders, “you can carry only the number of passengers that you have seatbelts and approved and suitable child car seats for.”
If you are a provisional P1 licence holders (red Ps) under 25 years of age, only one of your passengers can be aged under 21 if you are driving between 11pm and 5am.
How do you find a good mechanic?
Justin from NSW Roads and Maritime Services says that word of mouth is usually the best.
Can we get your opinion on window wipers?
Justin from RMS says the cheaper the better, then you can replace them more often. Opposite of tyres - get good tyres.
Is it illegal to go too slow on a highway?
Yes, it is. Especially in the right lane.
What is the penalty for hitting cyclists?
If the cyclist was hit as a result of negligent, furious or reckless driving, there could be a penalty of up to $5,500 and 2 years jail (for a 2nd offence).
There is a penalty of up to $5,500 and 2 years jail for not stopping and assisting someone after impact causing injury or death.
If I’m in a situation where I can't pull over or stop, can I call the police while driving? Assuming my passenger can’t.
Current legislation does not permit an L or P licenced driver to use their mobile phone in any way. Find a safe place to stop and turn the engine off in the event of an emergency.
Can I use apple car play in my car while on my P’s?
In New South Wales, it is illegal for a P-plater to have their phone connected to their head unit via Apple CarPlay. According to the Service NSW website, “[Learner, P1 and P2 drivers] must not use a mobile phone while driving, even when you’re stationary, for example, stopped at lights or stuck in traffic. This includes texting, phone calls, music, emailing, social media, using the internet, maps and navigation or photography.
“This applies to mobile phones that are handheld, in a phone holder or hands-free, for example, via Bluetooth.”
That means you cannot connect your phone to any radio via an AUX cable, Bluetooth, or Apple CarPlay.
All drivers are permitted to use a GPS device that isn't a mobile phone, as long as the device is mounted to the vehicle and doesn't obscure the driver’s view of the road.
How do I listen to music if I can’t use Bluetooth?
You can set up your phone to listen to music/podcasts before you start driving, but then put it away so it doesn't distract you. You can pull over and park out of the line of traffic to use your phone, but not while driving
Are p platers allowed to drive a v8?
Both P1 provisional licence holders and P2 provisional licence holders are banned from driving high performance vehicles that have:
- a power to tare mass ratio of greater than 130kW per tonne
- modified engines that need to be approved by an engineer, or other vehicles classified as high performance.
If you're a P1 or P2 provisional licence holder and want to check if you're allowed to drive a certain vehicle, you can do this online.
https://www.service.nsw.gov.au/transaction/check-prohibited-vehicles-for-provisional-p1-and-p2-drivers
What should I do if the driver in front of me is being stupid and trying breakcheck, tailgate, or other similar things?
Remain calm and don’t change your own driving behaviour in response to the person tailgating you. If you’re able to, indicate and change lanes so that the person tailgating you can pass. Don’t engage with the person to avoid escalating the situation into a road rage incident.
Avoid slowing down or flashing your brake lights, as this may escalate the situation. Rather than taking matters into your own hands, report the driver to police or the business to which the vehicle belongs.
If you've witnessed dangerous driving and the driver is unknown to you, safely pull over and call the Police Assistance Line on 131 444. Or have a passenger take down the registration number and make/model of the car that is tailgating you if their behaviour is aggressive.
https://www.mynrma.com.au/cars-and-driving/driver-training-and-licences/resources/how-to-deal-with-tailgating-drivers#:~:text=Remain%20calm%20and%20don%27t,this%20may%20escalate%20the%20situation.
What if I need to drive home from school tired?
Visit Remember to Stop, Revive, Survive | Driver Reviver Rest Stops for more info on the following advice:
Don't trust your tired self.
When you're preparing to drive, consider your own level of tiredness before you get behind the wheel, as well as during the drive. With fatigue accounting for almost 20 per cent of fatal road accidents in NSW, it's no wonder that it's one of the big three killers on our roads.
Research shows that being awake for 17 hours can have the same effect on your driving as a BAC (blood alcohol concentration) of 0.05, while going without sleep for 24 hours has the same effect as a BAC of 0.1 - double the legal limit.*
Sleep is the only cure for tiredness so make sure you're well rested before heading out. Many drivers like to ‘beat the traffic’ or get a ‘head start’ on their trip by leaving early in the morning; this can be dangerous. Travel at times you would normally be awake.
Don't plan to drive for long periods overnight. If you are facing a long holiday drive, book an overnight stop and extend the road trip.
* Source: National Library of Medicine.
Take breaks every two hours.
Before you set out on a long drive, plan your route and also use Transport for NSW's interactive map of rest areas to decide which rest stops you'll take. Have a discussion with your passengers to choose a spot of interest and to see if anyone wants to share the driving. To maintain safe energy levels, it's recommended you take a 15-minute break every two hours.
Make use of the rest areas and driver reviver sites scattered throughout the country to take regular breaks, stretch your legs, and get a breath of fresh air. Some sites also offer free tea, coffee and biscuits, shower facilities, shade, and water.
Don't 'push through' - stop and enjoy the journey.
On the road, we have the opportunity to reconnect with family and friends and help local communities by stopping and spending a few dollars. If you feel like you are in a rush, it can seem wise to 'push through' rather than stop over. This is when accidents are most likely to happen. But if you approach the road trip like a journey to enjoy, you will discover new experiences.
Check out our road trip itineraries and local's guides to help with planning and inspiration. You can also use the my nrma app to find the cheapest fuel in your areas, as well as discounted accommodation, attractions and food.
Should a driver be driving dangerously and are noncompliant with pulling over and letting you out, is it advised to forcefully take control to stop the car? (obviously force isn’t the answer – but if someone isn’t pulling over when you’ve asked them to, what can someone do in this situation?)
Practise having these tough conversations before getting into the car with a young or inexperienced driver. You both have a shared responsibility to help each other get where you are going safely. It is not advised to attempt to take control of the car as a passenger. Saying something such as, “I am going to be sick” may help the driver understand the implications of the situation. After all, no one wants to clean up vomit from their car!
Can you get PTSD from a car crash, if so what are the effects of that?
Road trauma can be very scary, even if you aren’t directly involved. Always seek advice from a counsellor or medical professional so you can get the help you need to deal with the aftermath of emotionally intense events.
Can RBTs break/show inaccurate results, and say I'm drunk when I'm not? Other than Bitters, perfumes, and mouthwash, are there other things that could make you fail a RBT preliminary test?
In Australia, all learner, P1/P2 provisional, probationary, or restricted drivers must have a blood alcohol concentration (BAC) of 0.00. Sometimes when a young driver is breathalysed as part of a random breath test (RBT) there are a number of things that could cause a positive reading (i.e., over 0.00) in the preliminary test even if you haven’t drunk alcohol.
https://darta.net.au/real-deal-on-drugs/can-using-mouthwash-cause-a-positive-rbt-what-about-an-up-go/
Any cakes/ desserts/ coffee that contains alcohol. Any medications that contain alcohol such as cough medicine, homeopathic remedies with an alcohol base.
alcohol based ear drops applied shortly before the test will show up in the air around the breathalyzer.
Do cops choose who to test for drugs like they do for RBT?
Like RBTs, police can pull a driver over and test for drugs anytime or anywhere. They might target certain locations, events or dates (e.g. outside music festivals), but generally, like RBT, you can’t tell where mobile road side drug testing will occur.
See here for more about Drugs and driving from the NSW Centre for Road Safety.
Can cannabis be found in a RBT test?
The drug test is a different test than the one for alcohol (an RBT test). The drug test is often done straight after the alcohol RBT by police. Cannabis can be found in the Mobile Drug Test (MDT).
If you inhale weed from second hand smoke, will that show up on a MDT?
It could show up depending on how much second hand smoke you inhale, what is the concentration of THC in the smoke and how well ventilated the room/space you are in is.
If you were in a close room with lots of smoke it might be more of a problem. One study found that some non-smoking participants exposed for an hour to high-THC marijuana (11.3% THC concentration) in an unventilated room showed positive urine tests in the hours directly following exposure.
Another study showed that non-smoking people in a confined space with people smoking high-THC marijuana reported mild effects of the drug and displayed mild impairments in motor tasks.
However, the study found that “positive tests are likely to be rare, limited to the hours immediately post-exposure, and occur only under environmental circumstances where exposure is obvious”.
Can I drive the next morning?
If you have a big night of drinking, it can take more than 18 hours for your Blood Alcohol Concentration (BAC) to get back to zero.
Lots of people get booked for being over the limit the day after drinking, even if they feel like they are safe to drive.
As an L or P plater, your BAC has to be zero. It’s best to not drive for most of the next day after a big night drinking.
Check out this info on ‘Getting back to zero’ from NSW Centre for Road Safety.
I can drink without registering in a breath test. Is there something wrong with me?
This sounds unusual, but it may be that you haven't drunk enough alcohol to register a BAC reading or that you haven’t waited long enough. However, it’s important to be aware that BAC machines in pubs and clubs aren't always accurate, so don't rely on them to drive. If you're a young person and have been drinking, don't drive!
Is nicotine in a drug test for underage drivers?
No
If I’m on my red Ps and driving (sober) but I have someone in my car with me that’s drunk will they be breath tested?
“Police are only able to breath test the driver of a vehicle. If they have reason to believe that a passenger in the car was in fact the actual driver, they can request a breath test from that person.”
Every police car is a mobile RBT. In NSW, police have the power to:
- Stop drivers at random to test for alcohol
- Arrest drivers who test over the legal limit
- Require a driver to take a sobriety test in certain circumstances
- Breath test any driver or supervising driver involved in a crash
Is it illegal to just be under the influence of a drug but not actually in possession of it?
It is illegal to be under the influence of a drug while driving and that's the most likely scenario to be charged for when driving. Read more here about mobile drug testing.
Can you get arrested for having cannabis smoke in your hair?
At the moment, MDTs are done through saliva testing only – hair samples are not collected during MDTs. However, if you were pulled over by a police officer for any reason and your hair did smell of cannabis, it could prompt that police officer to administer a MDT.
This Drug Info resource from the State Library of NSW explains the process of Mobile Drug Testing (MDT).
Can MDT detect mushies?
No. Mobile Drug Testing (MDT) at the roadside in NSW operates alongside Random Breath Testing (RBT) for alcohol and targets four illicit drugs - cannabis, cocaine, speed/ice and ecstasy.
MDT is increasing in NSW, with police undertaking up to 200,000 roadside drug tests each year. MDT is not the only method to detect drug driving. The second type of drug testing applies where a driver shows signs of being impaired by a drug at the roadside. Police can arrest you if they suspect you are driving while impaired by illegal drugs or medicines and you fail a sobriety assessment. You will be taken to a hospital to give samples of blood and urine for drug testing. This testing can detect a wide range of illegal drugs, as well as medicines.
Can you be mobile drug tested if you are a passenger?
Anyone who is operating or attempting to operate a motor vehicle may be required to undertake a roadside drug test, including any passenger acting as a ‘qualified supervising driver’ for a learner driver. Other vehicle passengers will not be required to undertake a Roadside Drug Test.
Is vaping legal for people our age? Can police remove vapes from people under 18 - are they legally able to do that?
Like for cigarettes, selling or supplying electronic cigarettes (e-cigarettes or vapes) to people 18 years and under is illegal. Police can seize an e-cigarette from someone who is suspected to be under the age of 18. This is legal under section 26(1) of the Public Health (Tobacco) Act 2008.
If I get tested for diabetes will they find weed in my system if I smoke it?
Most diabetes tests will be focussed on blood sugar level only. If a health worker is doing a comprehensive blood test they will normally ask pathology labs to look for things like cholesterol, blood sugar, iron levels etc. They don't check for drugs in the system, as that is not the purpose of these tests.
Why is ketamine not testable?
Ketamine can be tested for in specialised drug tests, but is not included in the current Mobile Drug Tests in NSW (i.e. saliva swabs). These only detect the most commonly used illicit drugs: cannabis, cocaine, speed/ice and ecstasy.
How long am I unable to drive for after consuming cannabis
Cannabis slows down your reaction time and reduces your ability to respond to situations. It also changes your perception of distance and time, lowers your concentration, reduces coordination and makes you drowsy. Cannabis users often don’t realise their driving is affected until they're faced with an unexpected situation. It's only after they're in danger that they realise they're incapable of making a quick or correct decision.
Roadside drug testing technology will detect recent usage of cannabis by detecting THC, the active ingredient in cannabis. THC will be able to be detected for several hours after use of cannabis, though the exact time will vary, for example depending on the amount and potency of the cannabis used.
The Road Transport Act 2013 stipulates that driving under the influence of any drug, medicinal or otherwise, that impairs driving is an offence. Cannabis (THC) can stay in the body system for a long time and be detected in small quantities. There is zero tolerance for THC traceability in drivers. The amount that can be detected after a period of time varies and can be different for different people and at different times for the same person.
Is it illegal to drive under the influence of amphetamines that I’ve been prescribed by a psychiatrist
Some medicines that can affect driving are:
• pain killers
• medicines for blood pressure, nausea, allergies, inflammations and
fungal infections
• tranquillisers, sedatives and sleeping pills
• diet pills
• cold and flu medicines.
Read the labels on your medication to determine whether it could affect your driving. If there’s a warning label that tells you not to drive, follow that advice.
Some labels say a medicine may affect your ability to drive. If you’re not sure, get advice from your doctor or pharmacist, and do not drive until you’ve done so.
Will you get punished if you are over the limit at the ambulance?
Ambulance officers come to save lives and don't punish anyone who needed their help after using alcohol or other drugs, so always call an ambulance if in need without thinking about police because they don't call Police unless there was an accident. If you drove, was involved in an accident and then police and ambulance crews came to the accident site, you will be first seen to by ambulance officers if you were injured. On this occasion (but only if this occurred) you would also be tested for drugs in your blood if you were the driver who was involved in the accident.
Can I drink alcohol and ride my bicycle?
Riding a bicycle under the influence of alcohol is a serious offence. You can be fined or imprisoned by a court if you are found to be drink riding.
Riding a bicycle under the influence of drugs or alcohol is illegal and dangerous for you and those around you.
Drugs and/or alcohol can inhibit your ability to respond quickly and safely in a hazardous situation. For more information see https://www.nsw.gov.au/driving-boating-and-transport/roads-safety-and-rules/bicycle-safety-and-rules/safe-riding#toc-drugs-and-alcohol
Can you be breath tested when riding a e-bike
Believe it or not, each state in Australia has explicit laws that state jumping on an e-scooter falls under the same rules that apply to drinking or drug use when behind the wheel of a car.
It is a full-on criminal offence that will stay on your record and affect you for the rest of your life, regardless of whether you have a driver's licence.
Can your phone be in your pocket while driving?
Technically yes if you don't use it, but it is obviously less comfortable than having it in your bag or the glove box and you'll have less temptation to use it if it’s not in your pocket.
Can you go on your phone while riding a push bike? Do these rules apply on a motorbike?
You can't use a mobile phone while riding a motorbike.
This excerpt is from Bicycle NSW website: “As a bike is classified as a vehicle in NSW, it is illegal to use most mobile device functions while riding, this includes video calling, texting, emailing, social media, web browsing, taking photos etc. Doing so can result in a fine of $349, or $464 if detected in a school zone.
Bike riders are only able to use a phone to make or answer calls, or play audio (including navigation). In order to do this, the phone must be secured in a cradle, or used without touching the device.
Bike riders can use a hands free device (such as voice activation) in order to control their mobile. However, they must not touch the phone while they are moving. Some helmets also have bluetooth functionality to connect your phone, and can be handy if needing to use your phone.”
Can P platers listen to music through their phones using aux or bluetooth?
No. P platers can’t listen to music through their phones – even if the phone was going to be used hands-free – while driving or stationary (like stopped at lights or stuck in traffic).
Can you give your phone to your friend to control music and stuff like that?
For P licence holders, no connection of phones through blue tooth is allowed, whether the passenger or driver are controlling the playlist.
Can you have your phone on a hands free phone holder to use google maps?
No. Restricted licence holders (L and P plates) are not allowed to use their phone at all while driving or riding. It doesn’t matter if it’s in a holder, or in your glove box and connected by Bluetooth, you can’t use it.
Can you wear a smartwatch while driving, if your phone is in the glove box?
No. The rules for mobile phones apply to smartwatches too. As an L or P plater you can’t use a smartwatch while driving or stationary in a car.
On an L or P plate with a NSW license can you drive at 110km/hr in Queensland?
No. The maximum speed limit restrictions in NSW for L and P platers apply when driving in other states and territories. So in all Australian states and territories, NSW Learner and Provisional P1 licence holders can drive to a maximum of 90km/h and Provisional P2 licence holders up to 100 km/h. See the Road Users’ Handbook for more information.
Can I kick someone out on the highway if they are being to annoying and distracting?
It's never a good idea to abandon a person on the side of the road. If you have clearly asked the person to stop distracting you and they persist, the safest thing to do is to find a safe place to pull over off the road and wait until the person calms down, then drive them to a safe place where they are not at risk, or to their home.
Do you have to indicate off roundabouts?
So other drivers know what you intend to do, you must indicate when turning at a roundabout. Continue to indicate as you turn. When you leave, you must indicate left, if practical. Stop indicating as soon as you have left the roundabout.
Can you get in legal trouble for having an open container of alcohol despite not drinking any ( Also proven by a perfect BAC check)?
Visit Alcohol & driving | Transport for NSW for more information on the current legislation around alcohol and driving. At this time, the law states that:
Zero BAC applies to all:
- learner drivers or riders
- provisional 1 drivers or riders
- provisional 2 drivers or riders
- visitors holding an overseas or interstate learner, provisional or equivalent licence.
Headspace
Head to Health
NNSWH AOD Youth Counselling
Mental Health Access Line
Lifeline
Family Drug Support
ADIS – Alcohol and other Drug Information Service
Young people and alcohol & other drugs
NSW Quitline | Cancer Institute NSW
Your Room | NSW Health and the Alcohol And Drug Information Service
The Alcohol and Drug Foundation - Alcohol and Drug Foundation
Who do you turn to if you can’t trust peers?
Think about any person who you feel you can trust and talk openly too. It could be a teacher, an Aunt or Uncle, a family friend, a sports coach - anyone who you trust to give you good advice.
You can always call Lifeline or Black dog or download an app such as the Clearly Me app from Black Dog Institute.



















